|
Our new paper on American uptake of booster was just published in Vaccine. Please find the abstract below:
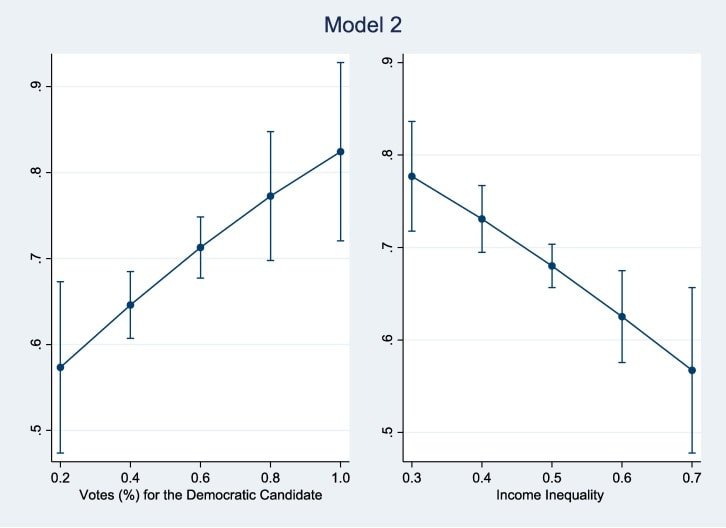
"The COVID-19 pandemic has posed an unprecedented impact on Americans for over three years. To control the damage, a booster shot becomes increasingly necessary because the efficacy of the initial vaccine is waning and new variants of the virus are emerging. This study aims to understand factors at both individual and state levels that influence one’s decision to take the monovalent booster. We merged data from a national survey administered in the Spring of 2022 with state-level indicators of the political climate, income inequality, and public health conditions. Multilevel logistic regression is adopted for statistical estimation. Findings show contrasting effects of the social network. More vaccinated people in one’s network promote booster uptake, while more family members and close friends who contracted the virus in one’s network inhibit booster uptake. In addition, residents of states with more votes for the Democratic candidate in the 2020 general election are more likely to take the booster. Meanwhile, residents from states with high income inequality are less likely to become boosted. This study identified multilevel determinants of the individual decision to receive the monovalent COVID-19 booster. The results imply the need to leverage the social network, weaken partisanship salience, and reduce income inequality to encourage booster uptake."
2 Comments
Our new paper, entitled "Understanding the Influence of Political Orientation, Social Network, and Economic Recovery on COVID-19 Vaccine Uptake among Americans" has been published online in Vaccine (Impact factor: 3.641). Below please find the abstract:
"The COVID-19 pandemic poses unprecedented risks to the well-being of Americans. To control the pandemic, a sufficient proportion of the population needs to be vaccinated promptly. Despite the proven efficacy and widespread availability, vaccine distribution and administration rates remain low. Thus, it is important to understand the public behavior of COVID-19 vaccination. This study aims to identify determinants at multiple levels that promote or inhibit one’s vaccine uptake. We combine individual-level data from a national survey conducted in the summer of 2021 with corresponding state-level indicators. Findings of multilevel logistic regression show that political orientation, social network, and economic recovery altogether have significant influence. We articulate that individual decisions to take the vaccine are a function of their personal characteristics and are also rooted in their home state’s political, public health, and economic contexts. These findings contribute to the literature and have policy implications. Knowledge of the profiles among people who take/refuse the vaccine provides essential information to leverage certain factors and maximize vaccine uptake to mitigate the pandemic’s devastating impact." Our paper entitled "Understanding American public support for COVID-19 risk mitigation: The role of political orientation, socio-demographic characteristics, personal concern, and experience" has been published the International Journal of Public Health (Impact factor: 3.38). Below please find the abstract:
"Objectives: COVID-19 is the most challenging public health crisis in decades in the United States. It is imperative to enforce social distancing rules before any safe and effective vaccines are widely available. Policies without public support are destined to fail. This study aims to reveal factors that determine the American public support for six mitigation measures (e.g., cancel gatherings, close schools, restrict non-essential travel). Methods: Based on a nationally representative survey, this study uses Structural Equation Modelling to reveal the relationships between various factors and public support for COVID-19 mitigation. Results: 1). Democrats are more likely than Republicans to support mitigation measures; 2).Favorability towards the political leader (Biden or Trump) can slant public support for COVID-19 mitigation measures among different segments of the public; 3). Indirect experience, rather than direct experience with COVID-19 can motivate people to support mitigation; 4). Concern for COVID-19 is a strong motivator of support for mitigation. Conclusion: Political polarization poses an enormous challenge to societal well-being during a pandemic. Indirect experience renders COVID-19 an imminent threat." Our new paper entitled "Understanding the effects of individual and state-level factors on American public response to COVID-19" has been accepted for publication in American Journal of Health Promotion (Impact factor: 2.87). Below please find the abstract:
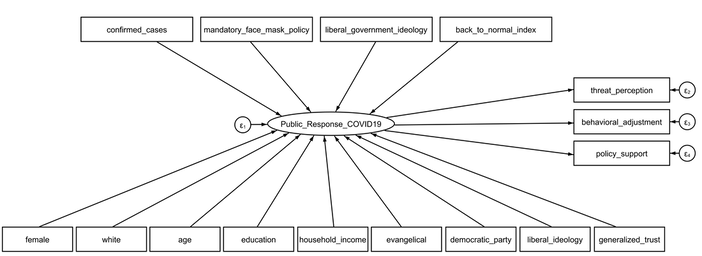
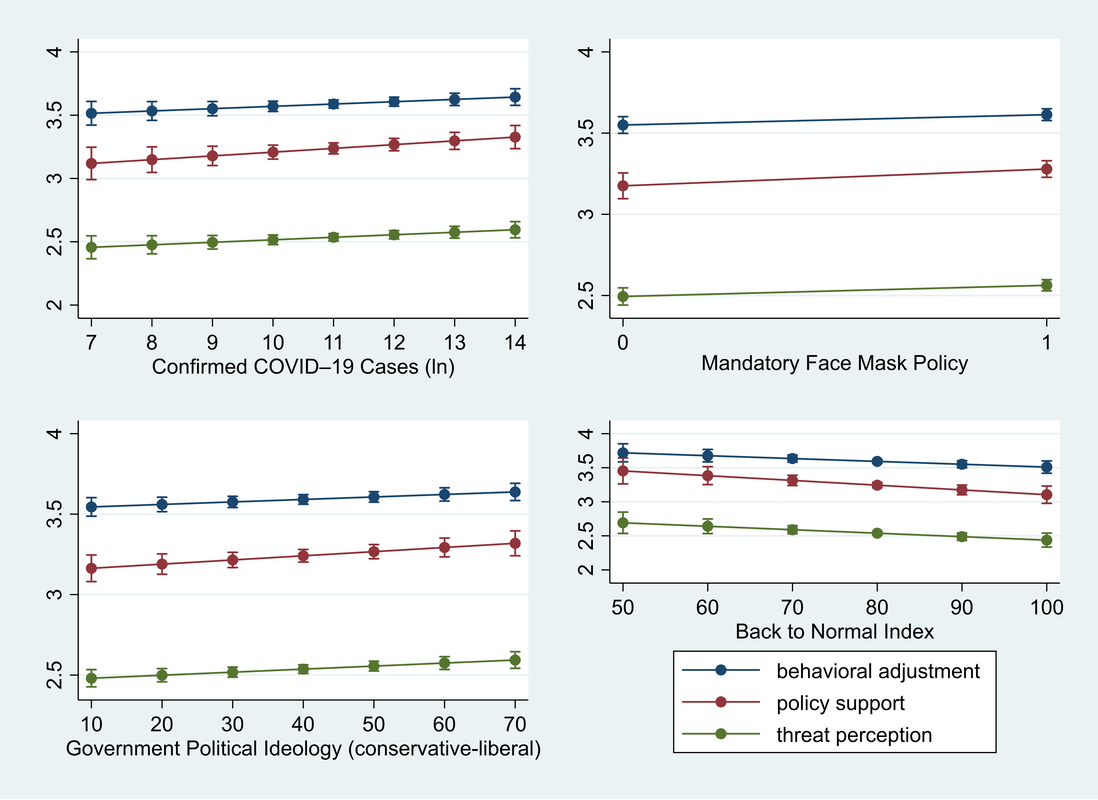
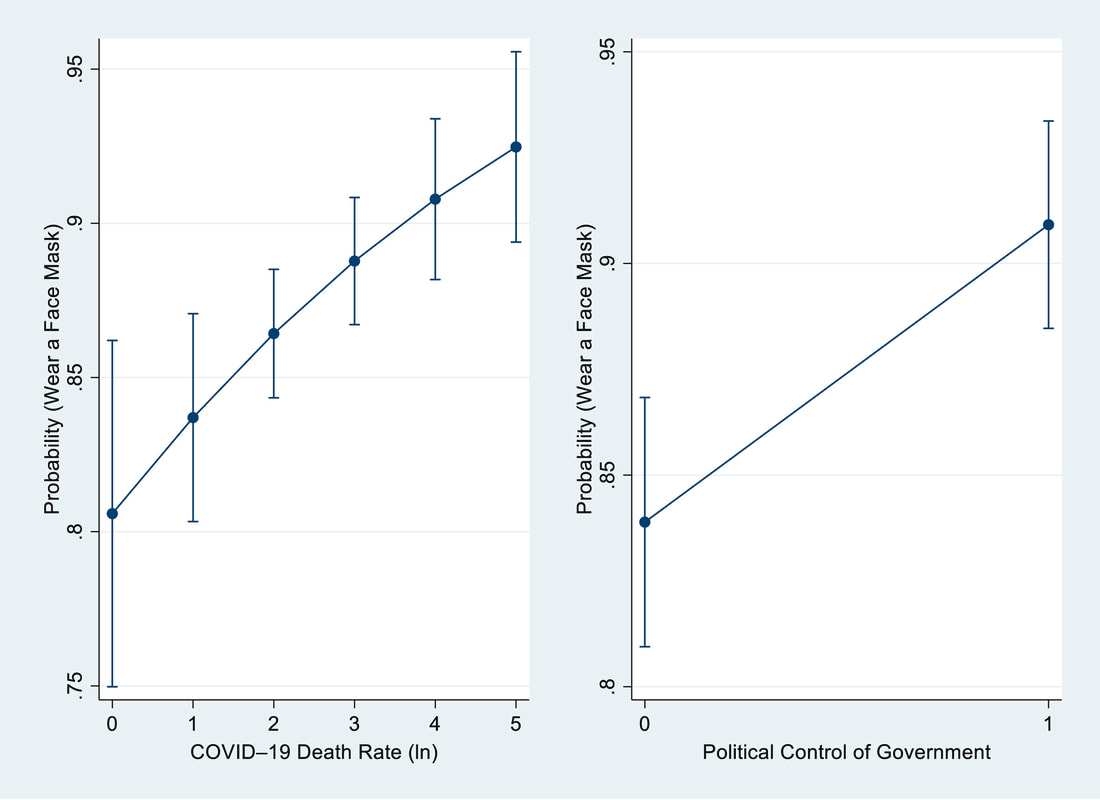
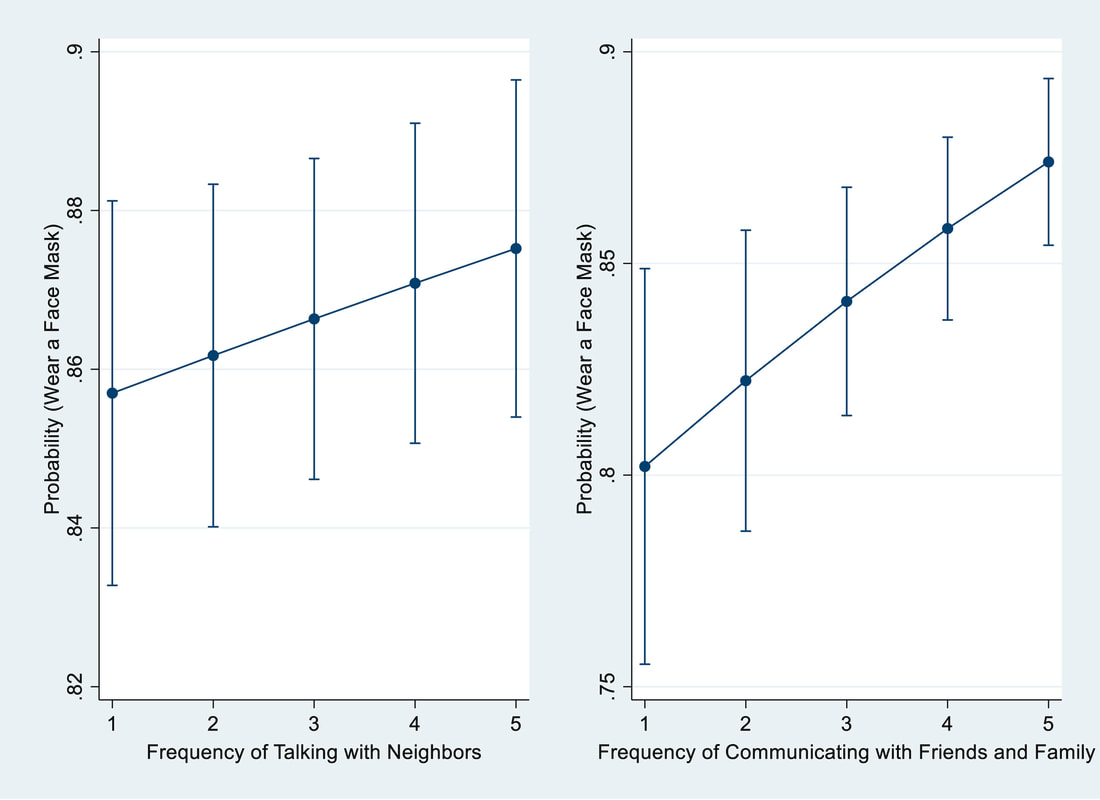
"Purpose: To examine multilevel predictors on American public response to COVID–19. Design: Multilevel study. Setting: A national survey was conducted by Qualtrics from August 24 to September 11, 2020. The state-level variables were constructed on data from multiple sources. Subjects: 2,440 respondents 18 years and older from all 50 states and D.C. Measures: The outcome variable is the public response to COVID–19 measured by threat perception, behavioral adjustment, and policy support. The predictors include individual-level sociodemographic factors and state-level indicators about public health conditions, political context, and economic recovery. Analysis: Multilevel structural equation modeling is used for statistical estimation. Results: People from states with more COVID–19 cases (β=0.020, p<0.1), mandatory face mask policies (β=0.069, p<0.05), and liberal governments (β=0.002, p<0.05) are more likely to respond while people from states whose economies have recovered closer to the pre-pandemic level are less likely to do so (β=-0.005, p<0.05). Regarding individual-level predictors, older people (β=0.005, p<0.001) and people with better education (β=0.029, p<0.01), leaning toward the Democrat Party (β=0.066, p<0.001) and liberal political ideology (β=0.094, p<0.001), and have stronger generalized trust (β=0.033, p<0.001) are more likely to respond than their counterparts. Conclusion: Differences in the public response to the pandemic stem from variations in individual characteristics and contextual factors of states where people live. These findings contribute to the rapidly growing literature and have implications for public health policies." 2/15/2021 0 Comments Our new paper in Health and Place Our new paper entitled "Understanding the influence of contextual factors and individual social capital on American public mask wearing in response to COVID-19" has been published in Health and Place (Impact Factor: 4.078) . Below please find the abstract: "The COVID–19 pandemic poses unprecedented risks to the health and well-being of the entire population in the U.S. To control the pandemic, it is imperative for individuals to take precautionary behaviors (e.g., wearing a mask, keeping social distance, washing hands frequently, etc.). The factors that influence individual behavioral response thus warrants a close examination. Using survey data for respondents from 10 states merged with state-level data, our study represents a pioneering effort to reveal contextual and individual social capital factors that explain public mask wearing in response to COVID–19. Findings of logistic multilevel regression show that the COVID–19 death rate and political control of government at the state level along with one’s social capital at the individual level altogether influence whether people decide to wear face masks. These findings contribute to the rapidly growing literature and have policy implications for mitigating the pandemic’s devastating impact on the American public." 9/16/2019 2 Comments Our new paper is published in the International Journal of Environmental Health Research Our new paper has been published in the International Journal of Environmental Health Research. In this paper, we examined potential factors that could affect community-level mental health across the United States. Here is the the summary:
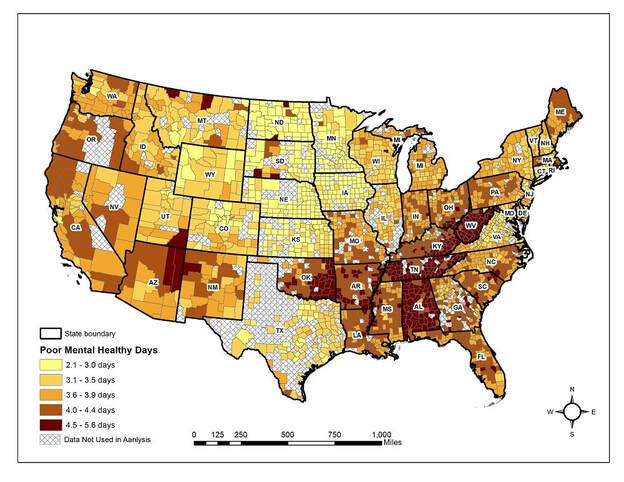
"Mental health studies have underscored the hazardous conditions of each phase of life, from youth and pre-adulthood through adulthood in the United States. This situation calls for increased public awareness of the mental health issue and better understanding of the significant factors associated with mental health hazard. The main objective of this spatial epidemiological research is to gain greater insights into the geographic dimension displayed by the different duration of mentally unhealthy days (MUDs) across U.S. counties. Using Behavioural Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) data in 2014, we examine main factors of mental health hazard including health behaviour, clinical care, socioeconomic and physical environment, demographic, community resilience, and extreme climatic conditions. In this study, we take complex design factors such as clustering, stratification and sample weight in the BRFSS data into account by using Complex Samples General Linear Model (CSGLM). Then, spatial regression models, spatial lag and error models, are applied to examine spatial dependencies and heteroscedasticity. Econometric analysis underscores that all categories of air pollution, community resilience, and sunlight variables tested are significant push factors of mentally unhealthy days (MUDs) duration. Results of the geographic analyses indicate that counties with lower air pollution (PM2.5), higher community resilience (social, economic, infrastructure, and institutional resilience), and higher sunlight exposure had significantly lower average number of MUDs reported in the past 30 days. These findings suggest that policy makers should take air pollution, community resilience, and sunlight exposure into account when designing environmental and health policies and allocating resources to more effectively manage mental health problems." The following figure is from this paper (Ha and Shao 2019) |
|


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed